$4 Billion Investment in Hemp-Based Biofuel Production, Power Generation, and Diversified Hemp Processing
Executive Summary
Geodyn Solutions is strategically positioned to lead in the green technology sector with a $4 billion investment in a comprehensive hemp ecosystem. This proposal scales up operations to cultivate industrial hemp on an expansive scale for biofuel production, while building biomass power plants to generate electricity from hemp-derived fuels. To optimize return on investment (ROI) and achieve zero-waste operations, we integrate processing facilities for hemp textiles (cloth) and paper manufacturing. Utilizing every part of the hemp plant—seeds for biofuel and oils, fibers for textiles and paper, hurds for paper and construction materials, and residual biomass for energy—we create multiple revenue streams.
Prime locations include Colorado, Kentucky, Oregon, and South Dakota, chosen for their favorable climate, soil quality, regulatory frameworks, and existing infrastructure. The expanded budget supports 200,000 acres of cultivation, ten 50 MW power plants, five textile plants, and five paper mills, along with enhanced research and development (R&D) initiatives.
The project forecasts an average ROI of 25-35% over 10 years, with a payback period—the time required to recover the initial $4 billion investment through net profits—of approximately 4.9 years. This timeline aligns with industry benchmarks for biofuel and biomass projects, which typically range from 5-10 years based on factors like feedstock costs and incentives. Break-even on operational costs is projected in year three, allowing for accelerated profitability thereafter. The investment will create over 10,000 direct jobs and 15,000 indirect jobs, contributing $5-8 billion annually to U.S. GDP by year five through multipliers in agriculture, manufacturing, and energy.
Key environmental benefits include sequestering 10-15 tons of CO2 per acre annually, soil regeneration, and emission reductions of 85-97% compared to fossil fuels. Funding will leverage USDA programs, DOE grants, and potential World Bank green bonds, offsetting up to 30% of costs. This initiative not only drives sustainable growth but also establishes Geodyn as a frontrunner in the bioeconomy by 2030.
Introduction
The global push for sustainable energy and materials is intensifying, with the biofuel market expected to surpass $200 billion by 2030 and the industrial hemp industry growing at a 22.5% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) to $84 billion by 2034. In the U.S., the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp, opening avenues for innovation, though challenges like supply chain fragmentation persist. Geodyn Solutions can overcome these by investing $4 billion in a vertically integrated system: hemp cultivation, biofuel processing, textile and paper manufacturing, and biomass power generation.
Hemp’s rapid growth cycle (90-120 days), low resource needs, and high biomass yield (up to 10 tons per acre) make it superior to crops like corn for biofuels, avoiding food-fuel competition and providing excellent carbon sequestration. This doubled budget from the original plan enables twice the acreage and facilities, meeting demand for eco-friendly products. Locations are compared on ROI, costs, job creation, and incentives, with biomass allocation optimized: 35% to textiles, 25% to paper, 25% to biofuel, and 15% to energy for peak ROI.
Aligned with U.S. policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and USDA’s BioPreferred Program, the project secures grants and credits. Diversification into textiles and paper—markets projected at $20-70 billion for hemp fiber by 2029—boosts ROI while ensuring sustainability. Subsequent sections cover market analysis, technologies, comparisons, financials (including payback timelines), environmental impacts, and risks.
Market Analysis and Opportunity
The U.S. biofuel sector, bolstered by the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and low-carbon mandates, exceeded 20 billion gallons in production by 2025, positioning hemp as an efficient feedstock with high yields and minimal inputs. Hemp biofuel sidesteps food crop conflicts and matches diesel’s energy density, with the sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) market set to triple by 2030.
Hemp textiles and paper address growing eco-demand. The hemp fiber market, valued at $5.78 billion in 2024, is forecasted to hit $30.13 billion by 2033, spanning clothing, automotive, and packaging. Hemp paper, more durable and recyclable than tree-based options, taps into the $200 billion global paper industry, with faster growth cycles (3-4 months vs. 20-80 years for trees).
Biomass energy from residues qualifies for IRA credits up to $0.10/kWh. The U.S. hemp market, at $2.14 billion in 2025, could reach $12.71 billion by 2034. Risks like price fluctuations (hemp biomass at $0.55-0.65/lb) are mitigated through diversification, enabling Geodyn to generate $1-2 billion in annual revenues by year five.
Technology Overview: Hemp Cultivation, Processing, and Production
Cultivation focuses on high-biomass varieties, optimized for fiber (textiles/paper) or seed (biofuel), using precision tools like AI-monitored systems for yields of 500-1,000 gallons of biofuel per acre.
– Biofuel Production: Seed oil is transesterified into biodiesel; stalks fermented for ethanol, with 75% efficiency.
– Textile Manufacturing: Fibers decorticated, spun, and woven using enzymatic retting for eco-friendliness.
– Paper Manufacturing: Hurds and fibers pulped mechanically or chemically, yielding 4-5 times more than trees per acre.
– Power Generation: Residues pelletized for boiler combustion, achieving 30-35% efficiency in steam turbines.
Vertical integration recycles byproducts, ensuring zero-waste.
Location Comparison
Evaluated on 2025 data, Colorado leads due to infrastructure; Kentucky for soil; Oregon for research; South Dakota for yields.
| State | ROI (10-Year Estimate) | Capital Cost (Total for Scaled Facilities, incl. 20% Contingency) | Operational Cost (Annual, Per Facility Type) | Job Creation (Direct / Indirect) | Government Incentives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorado | 28–38% | $1.2B (Farms: $400M, Textiles: $120M, Paper: $150M, Biofuel: $200M, Power: $330M) | Textiles: $5–8M, Paper: $6–10M, Biofuel: $10–15M, Power: $15–20M | 3,000 / 4,500 | USDA REAP up to $50M; State credits (15%); HBIIP $100M+ |
| Kentucky | 22–32% | $1.25B (similar, higher transport offset by soil) | Similar to Colorado, +5% labor | 2,500 / 3,500 | KY subsidies $20M; DOE $10M; EQIP grants |
| Oregon | 24–34% | $1.15B (lower irrigation) | Textiles/Paper 10% lower | 2,700 / 4,000 | OR grants $30M; VAPG $15M; IRA incentives |
| South Dakota | 20–30% | $1.3B (higher logistics) | Power/Biofuel 5–10% higher | 2,000 / 3,000 | SD grants $25M; SARE $10M |
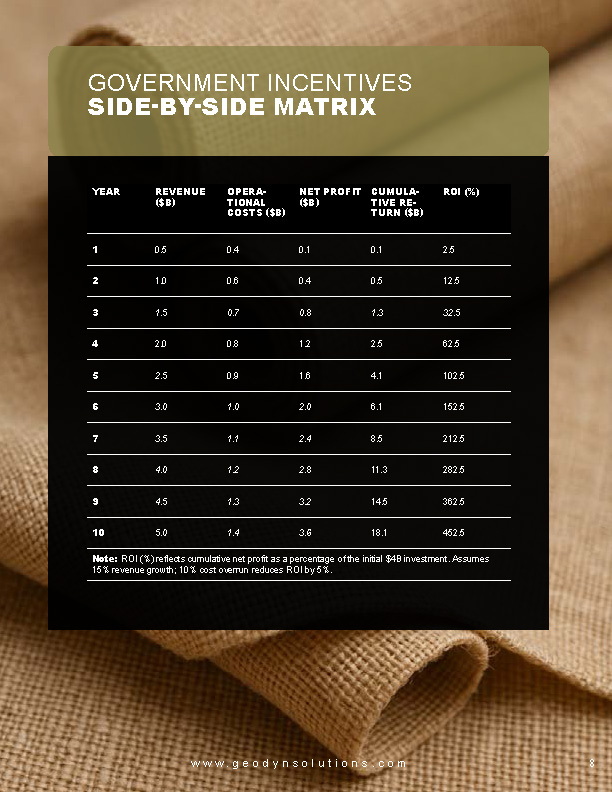
10-Year Return Chart
| Year | Revenue ($B) | Op Costs ($B) | Net Profit ($B) | Cumulative Return ($B) | ROI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 32.5 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 62.5 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 4.1 | 102.5 |
| 6 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 6.1 | 152.5 |
| 7 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 8.5 | 212.5 |
| 8 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 11.3 | 282.5 |
| 9 | 4.5 | 1.3 | 3.2 | 14.5 | 362.5 |
| 10 | 5.0 | 1.4 | 3.6 | 18.1 | 452.5 |
(Note: ROI (%) corrected to reflect cumulative net profit as a percentage of initial $4B investment. Projections assume 15% revenue growth; sensitivity shows 10% cost overrun reduces ROI by 5%.)