Comparative $250 Million Biofuel-to-Power Proposal Geodyn Solutions: Industrial Hemp vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum – Dominican Republic
Executive Summary
Geodyn Solutions, in partnership with Dominican stakeholders, proposes a $250 million investment to establish a biofuel-to-power ecosystem in the Dominican Republic (DR). This project compares two strategic feedstock pathways:
Industrial Hemp – diversified model emphasizing nutraceuticals, textiles, biodiesel, and biomass electricity.
Sugarcane & Sorghum – high-volume energy model with ethanol, bagasse pellets, molasses, and baseload power.
Key Investment Metrics:
Power Output: 30 MW (240 GWh/year)
ROI: Hemp 28–33% vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum 30–40%
Payback: Hemp ~5.0 yrs vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum ~4.5 yrs
CO₂ Offset: 125,000–200,000 tons/year
Jobs: 1,500+ direct & indirect
Government Incentives: Up to $80M available
Feedstock Performance
| Criteria | Industrial Hemp | Sugarcane & Sorghum |
|---|---|---|
| Biomass Yield (t/ha/yr) | 13–15 | 60–100 (cane), 40–60 (sorghum) |
| Ethanol Potential (L/ton) | 300–400 | 400–700 |
| Electricity Output (kWh/ton) | ~1,250 | ~1,450 |
| ROI (15 yrs) | 28–33% | 30–40% |
| Payback Period | ~5.0 years | ~4.5 years |
Chart 1 – ROI vs Biomass Yield vs Ethanol Potential
This chart compares Industrial Hemp, Sugarcane, Sorghum, and other biomass feedstocks.
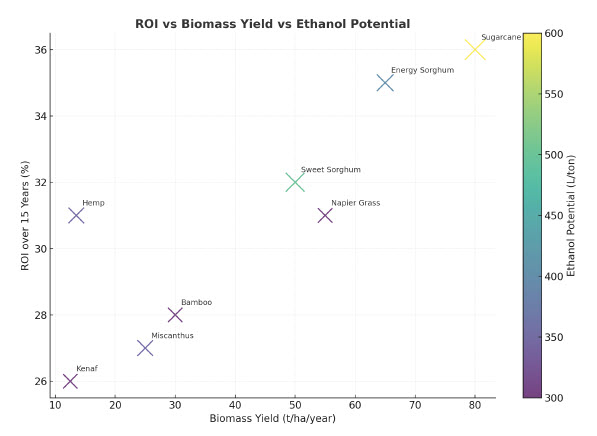
Insight: Sugarcane & Sorghum achieve higher yields and ROI, while Hemp offers strong diversification through co-products.
Co-Product Value Chains
Industrial Hemp
Seeds → Biodiesel & oils
Fibers → Textiles & pellets
Hurds → Hempcrete & ethanol
Flowers/Leaves → Nutraceuticals
Roots → Soil amendment & carbon credits
Sugarcane & Sorghum
Bagasse → Pellets & electricity
Molasses → Ethanol & animal feed
Sorghum Juice → Ethanol production
Residues → Nutraceuticals & compost
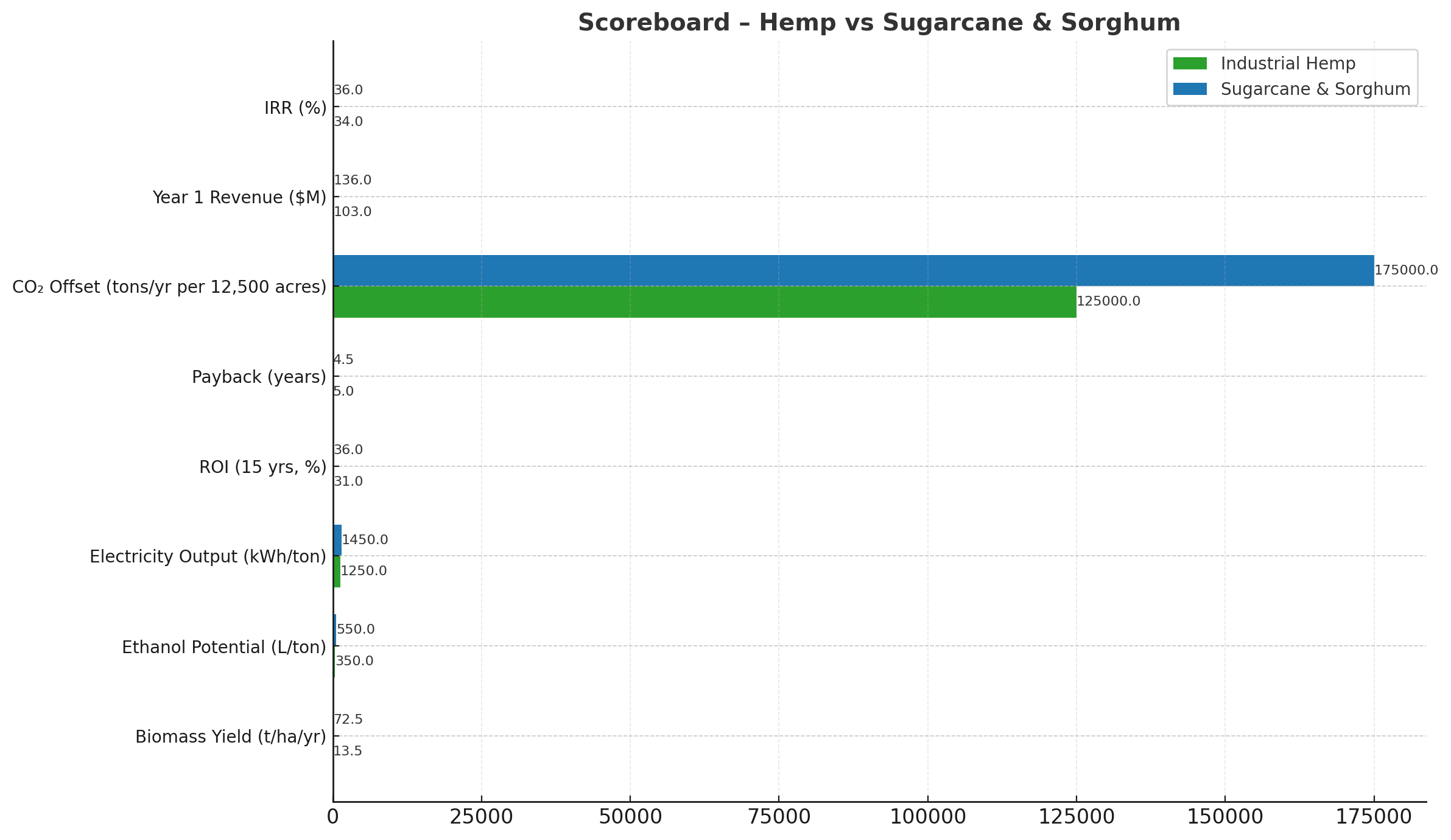
Chart 2 – Scoreboard: Hemp vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum
Side-by-side performance comparison of the two models.
Revenue Diversification
Chart 3 – 10-Year Projection
Hemp: Co-products (nutraceuticals & textiles) dominate long-term revenues.
Sugarcane & Sorghum: Ethanol and bagasse pellets lead, electricity provides a stable base.
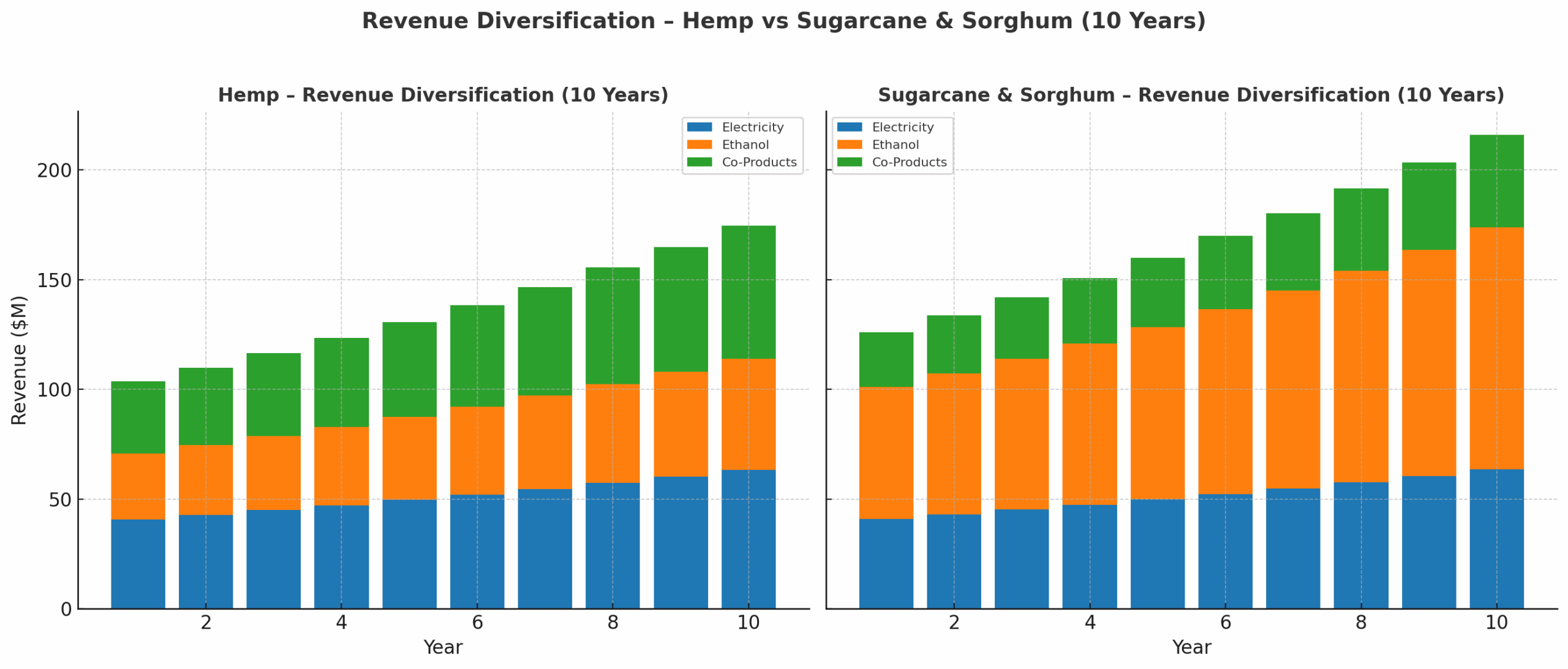
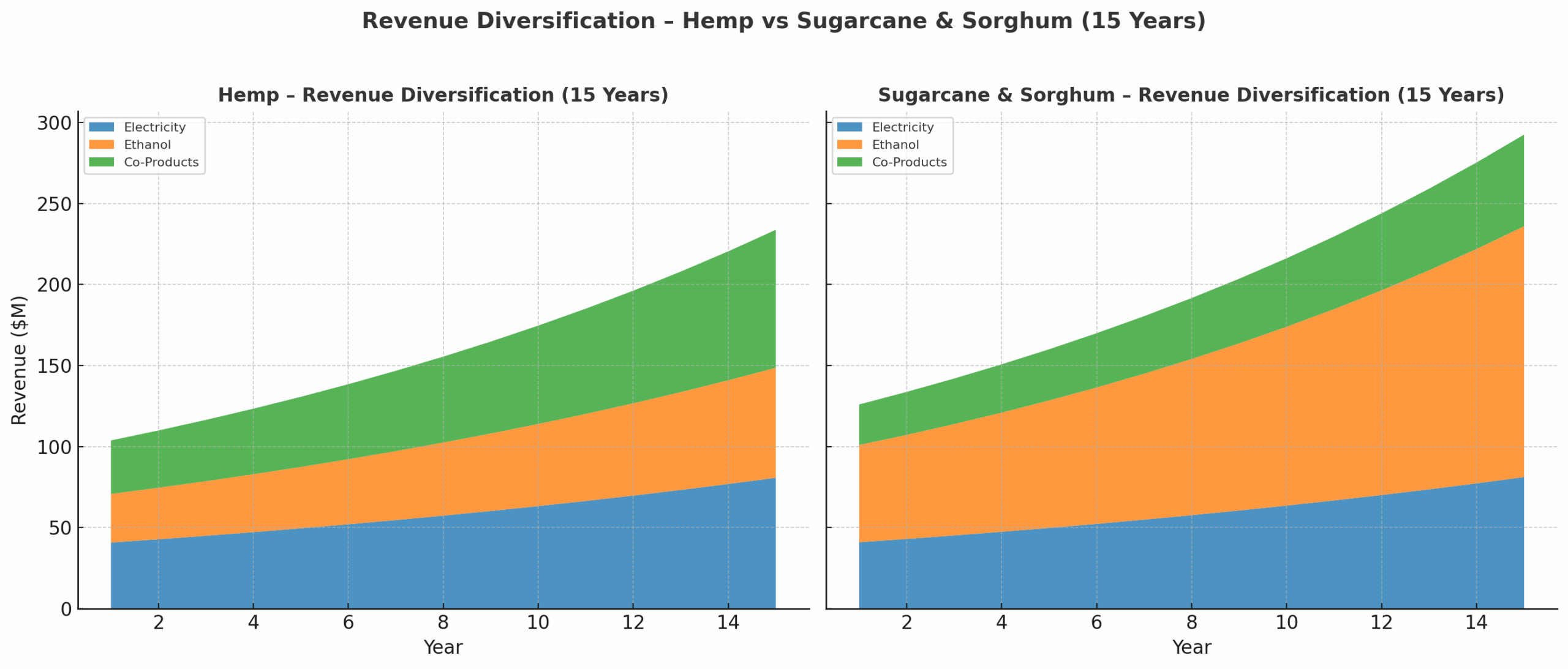
Chart 4 – 15-Year Projection
Long-term growth shows different strengths:
Hemp → Co-products steadily increase, becoming the largest stream.
Sugarcane & Sorghum → Ethanol scales fastest, co-products and electricity remain steady contributors.
Financial Overview
Capex: $250M (Land $15M, Facility $55M, Turbines $75M, Cultivation $35M, R&D $25M, Contingency $45M)
Opex: Hemp ~$60M/year; Sugarcane & Sorghum ~$65M/year
Year 1 Revenue: Hemp ~$103M vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum ~$136M
NPV: Hemp ~$480M vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum ~$520M
IRR: Hemp 34% vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum 36%
Payback: Hemp ~5 years vs. Sugarcane & Sorghum ~4.5 years
Environmental Benefits
Hemp: Sequesters 125,000–187,500 tons CO₂ annually; strong soil remediation impact
Sugarcane & Sorghum: Offsets 150,000–200,000 tons CO₂; rotational cropping supports soil fertility
Timeline
| Phase | Milestones | ETA |
|---|---|---|
| Permits & Funding | Site selection, EIA | Q4 2025 – Q1 2026 |
| Construction | Distillery & turbines | Q2 2026 – Q1 2027 |
| Pilot Operations | Initial planting & runs | Q2 – Q3 2027 |
| Scale-Up | First harvest & grid supply | Q1 2028 |
| Payback | Investment recovery | Q3 2030 |



