Geodyn Solutions Advanced Offshore Fish Farming Proposal for the Dominican Republic
Executive Summary
Geodyn Solutions proposes a $250M offshore fish farming operation in the Dominican Republic, integrating the most advanced aquaculture technologies to produce 30,000 metric tons of seafood annually while addressing environmental and health concerns. Inspired by cutting-edge global models , this project employs smart aquaculture systems, sustainable feeds, Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS), genomic selection, and algae integration. Fish waste is captured and processed into 6,000 tons of organic fertilizer and 3,000 tons of fish hydrolysate annually, creating a circular bioeconomy. With a 20% contingency, the project aims to create 600–800 jobs, achieve a 10-year ROI of 310%, and set a global standard for sustainable aquaculture.
Project Overview
Located 5–15 miles off the Dominican Republic’s southern coast, the project utilizes 60 fully submerged, hurricane-resistant net pens to cultivate high-value species (yellowtail, tilapia, cobia, and shrimp). It incorporates Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA), IoT-enabled smart systems, and a fleet of five hybrid vessels. A state-of-the-art processing facility produces export-ready products, while advanced waste capture systems ensure zero waste. The project aligns with global sustainability goals, minimizing environmental impact and enhancing seafood quality.
Key Objectives
- Produce 30,000 metric tons of seafood (25,000 tons fish, 5,000 tons shrimp) annually, with 70% processed for export.
- Create 600–800 direct and indirect jobs, boosting coastal economies.
- Convert 9,000 tons of fish and shrimp waste into 6,000 tons of fertilizer and 3,000 tons of hydrolysate.
- Minimize environmental impact through smart technology, RAS, and IMTA.
- Achieve a 10-year ROI of 310% with diversified revenue streams.
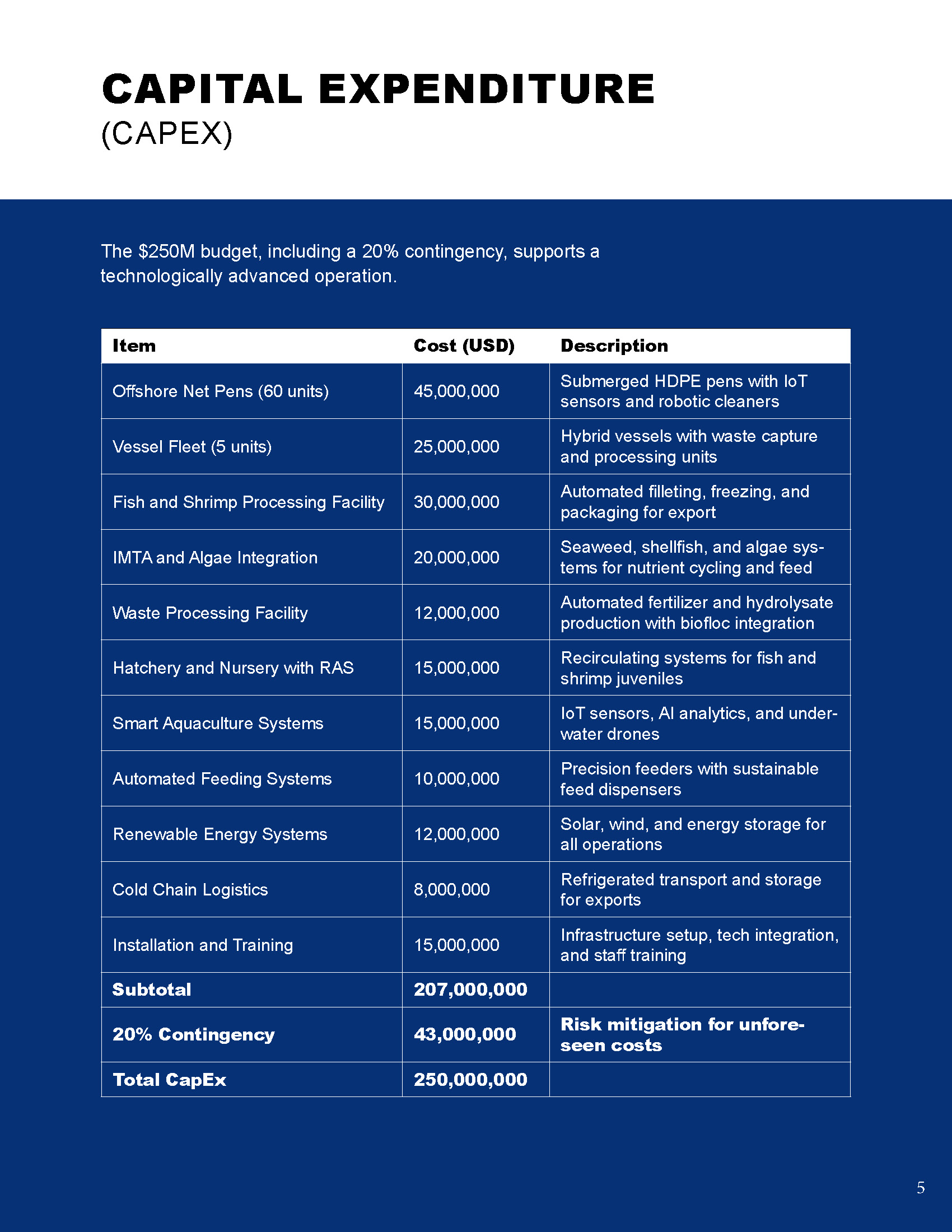
Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
The $250M budget, including a 20% contingency, supports a technologically advanced operation.
Item | Cost (USD) | Description |
Offshore Net Pens (60 units) | 45,000,000 | Submerged HDPE pens with IoT sensors and robotic cleaners |
Vessel Fleet (5 units) | 25,000,000 | Hybrid vessels with waste capture and processing units |
Fish and Shrimp Processing Facility | 30,000,000 | Automated filleting, freezing, and packaging for export |
IMTA and Algae Integration | 20,000,000 | Seaweed, shellfish, and algae systems for nutrient cycling and feed |
Waste Processing Facility | 12,000,000 | Automated fertilizer and hydrolysate production with biofloc integration |
Hatchery and Nursery with RAS | 15,000,000 | Recirculating systems for fish and shrimp juveniles |
Smart Aquaculture Systems | 15,000,000 | IoT sensors, AI analytics, and underwater drones |
Automated Feeding Systems | 10,000,000 | Precision feeders with sustainable feed dispensers |
Renewable Energy Systems | 12,000,000 | Solar, wind, and energy storage for all operations |
Cold Chain Logistics | 8,000,000 | Refrigerated transport and storage for exports |
Installation and Training | 15,000,000 | Infrastructure setup, tech integration, and staff training |
Subtotal | 207,000,000 | |
20% Contingency | 43,000,000 | Risk mitigation for unforeseen costs |
Total CapEx | 250,000,000 |
Advanced Technology Details
The project integrates the latest aquaculture innovations to ensure sustainability, efficiency, and quality.
- Smart Aquaculture Systems:
- IoT sensors monitor water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and salinity in real time, maintaining optimal conditions (e.g., 25–28°C, pH 7.5–8.5).
- AI-powered analytics predict disease risks and optimize feeding, reducing mortality by 30%.
- Submersible drones with 4K cameras provide 24/7 monitoring of fish health and pen integrity.
- Submerged Net Pens:
- 60 HDPE pens (50m diameter), submerged at 20–30m to avoid storms, equipped with anti-fouling coatings.
- Robotic net cleaners and dynamic mooring systems reduce maintenance costs by 25%.
- IoT-enabled pens adjust depth automatically based on weather data.
- Sustainable Feed Solutions:
- Algae-based feeds (40% of diet) and insect larvae (20%) replace 60% of fishmeal, reducing pressure on wild stocks.
- Feed fortified with omega-3 from on-site algae cultivation enhances fish nutritional profile.
- Automated feeders with sonar sensors deliver feed only when fish/shrimp are active, cutting waste by 20%.
- Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS):
- Hatchery and nursery use RAS with biofilters, UV sterilization, and oxygenation to recycle 95% of water.
- Reduces water use by 90% compared to traditional systems and prevents disease spread.
- Supports 20 million fish and 50 million shrimp juveniles annually.
- Genomic Selection for Breeding:
- Non-GMO genomic screening identifies fish and shrimp with superior growth (15% faster) and disease resistance.
- Breeding programs increase yield by 20% without genetic modification.
- Maintains genetic diversity to ensure long-term resilience.
- IMTA and Algae Integration:
- Co-cultivates seaweeds (e.g., Ulva), shellfish (e.g., mussels), and algae (e.g., Spirulina) to absorb nutrients.
- Algae provide 10% of fish/shrimp feed and sequester 20 tons of CO2 per hectare annually.
- Reduces nitrogen/phosphorus pollution by 50%.
- Eco-Friendly Shrimp Farming:
- Biofloc systems use beneficial bacteria to recycle shrimp waste into feed, reducing external feed needs by 30%.
- Vertical shrimp farming in stacked RAS units maximizes space and minimizes land use.
- Eliminates antibiotic use through probiotic-enhanced water treatment.
- Renewable Energy Systems:
- Solar arrays, offshore wind turbines, and lithium-ion storage power 85% of operations.
- Reduces carbon footprint by 45% compared to conventional aquaculture.
- Vessel Fleet:
- Five 70-meter hybrid vessels (diesel-solar) with onboard waste capture, refrigeration, and fish grading.
- Automated waste collection systems process 50 tons/day, reducing transport emissions by 30%.
- Fish and Shrimp Processing Facility:
- Processes 21,000 tons annually into fillets (60%), smoked products (20%), and frozen whole fish/shrimp (20%).
- Automated filleting machines achieve 95% yield; blast freezers ensure 18-month shelf life.
- Meets FDA, EU, and Codex Alimentarius export standards.
- Cold Chain Logistics:
- IoT-enabled refrigerated trucks and containers maintain -18°C for exports.
- Real-time tracking ensures traceability to US, EU, Asia, and Caribbean markets.
Fish Waste Capture and Fertilizer Production
Advanced waste capture systems create a zero-waste operation.
- Fish Waste Fertilizer:
- Annual waste: ~9,000 tons (30% of 30,000 tons, including fish and shrimp).
- 6,000 tons processed into organic fertilizer via high-capacity composting with biofloc integration.
- Supports local agriculture (e.g., coffee, cacao), reducing synthetic fertilizer use by 15%.
- Fish Hydrolysate:
- 3,000 tons of offal, heads, and processing trimmings processed via enzymatic hydrolysis.
- Produces liquid biofertilizer for high-value crops, enhancing soil microbial activity.
- Waste Capture Process:
- Vessels equipped with vacuum-based waste collection systems capture 95% of solid waste from pens.
- Onshore facility uses automated reactors, dryers, and odor-neutralizing systems.
- Biofloc systems recycle 20% of waste into shrimp feed, closing the nutrient loop.
- Environmental Impact:
- Zero waste discharge into marine environments.
- Wastewater treated and reused for facility operations.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Revenue from seafood, processed products, fertilizer, and hydrolysate yields a 10-year ROI of 310%.
Revenue Streams
- Seafood Sales (Raw): 9,000 tons at $5,000/ton = $45,000,000/year.
- Processed Seafood (Export): 21,000 tons (fillets, smoked) at $7,000/ton = $147,000,000/year.
- Organic Fertilizer: 6,000 tons at $500/ton = $3,000,000/year.
- Fish Hydrolysate: 3,000 tons at $1,000/ton = $3,000,000/year.
Financial Projections
- Annual Revenue: $198,000,000
- Annual Operating Costs: $58,000,000 (feed, labor, vessels, processing, AI, logistics)
- Annual Net Profit: $140,000,000
- Break-even Point: Year 3
- 10-Year Net Profit: $1,400,000,000
- ROI: ($1,400,000,000 – $250,000,000) / $250,000,000 = 310%
Job Creation
The project creates significant employment opportunities.
Role | Number of Jobs | Description |
Aquaculture Technicians | 150 | Manage pens, IMTA, and smart systems |
Vessel Crew | 100 | Operate vessels for waste capture and transport |
Processing Staff | 150 | Handle filleting, smoking, and packaging |
Waste Processing Staff | 80 | Produce fertilizer and hydrolysate |
Hatchery and RAS Workers | 60 | Manage fish and shrimp juveniles |
AI and Tech Support | 30 | Maintain IoT and automation systems |
Logistics and Cold Chain | 30 | Manage export transport |
Administrative and Sales | 30 | Oversee operations and global marketing |
Indirect Jobs (e.g., retail, export) | 150–170 | Support supply chain and distribution |
Total Jobs | 600–800 |
Environmental and Health Benefits
The project addresses aquaculture’s historical concerns with innovative solutions.
- IMTA and Algae Integration:
- Reduces nutrient pollution by 50–60%, protecting marine ecosystems.
- Algae enhance fish/shrimp omega-3 content by 20%, improving consumer health.
- Zero-Waste Operations:
- 9,000 tons of waste recycled into fertilizer and hydrolysate, eliminating ocean discharge.
- Biofloc systems recycle nutrients, reducing external inputs.
- Sustainable Feeds:
- Algae and insect-based feeds reduce fishmeal use by 60%, preserving wild stocks.
- Enhances seafood nutritional quality (e.g., higher DHA/EPA levels).
- RAS and Biofloc:
- RAS cuts water use by 90%; biofloc eliminates antibiotic needs in shrimp farming.
- Prevents disease spread, ensuring safer seafood.
- Low-Carbon Operations:
- Renewable energy powers 85% of operations, reducing emissions by 45%.
- Hybrid vessels and electric logistics minimize fuel use.
- Ecosystem Protection:
- Offshore pens and AI monitoring prevent escapes and overfeeding.
- Biodegradable packaging for processed products reduces plastic waste.
Implementation Timeline
Phase | Duration | Activities |
Planning and Permits | 12 months | Secure permits, finalize site selection |
Infrastructure Setup | 30 months | Install pens, vessels, RAS, and facilities |
Initial Operations | 12 months | Stock pens, begin IMTA, start processing |
Full Production | Year 4 | Reach 30,000 tons/year, optimize exports |
Conclusion
Geodyn Solutions’ $250M offshore fish farming project redefines aquaculture in the Dominican Republic with the most advanced technologies. By integrating smart systems, sustainable feeds, RAS, genomic selection, and zero-waste processing, the project delivers a 310% ROI, 600–800 jobs, and a sustainable model for global seafood production. We invite partnerships with government, exporters, and local communities to lead the future of aquaculture.